
Since entropy is a state variable, just depending upon the beginning and end states, these expressions can be used for any two points that can be put on one of the standard graphs. Using the ideal gas lawīut since specific heats are related by C P = C V + R. If Suniv is positive, then the process is spontaneous. Entropy is the measure of a system’s thermal energy per unit temperature that is unavailable for doing useful work. This is a useful calculation form if the temperatures and volumes are known, but if you are working on a PV diagram it is preferable to have it expressed in those terms. Solution We can assess the spontaneity of the process by calculating the entropy change of the universe. Making use of the first law of thermodynamics and the nature of system work, this can be written With kT/2 of energy for each degree of freedom for each atom.įor processes with an ideal gas, the change in entropy can be calculated from the relationship This gives an expression for internal energy that is consistent with equipartition of energy. The standard state entropy change for a reaction, S, can be calculated from data in thermodynamic tables in a manner similar to changes in enthalpy and.
#HOW TO CALCULATE ENTROPY CHANGE THERMODYNAMICS FREE#
Then making use of the definition of temperature in terms of entropy: To illustrate this concept, the equation relating free energy change to the enthalpy and entropy changes for the process is considered: G H T S G H T S The spontaneity of a process, as reflected in the arithmetic sign of its free energy change, is then determined by the signs of the enthalpy and entropy changes and. Expanding the entropy expression for V f and V i with log combination rules leads toįor determining other functions, it is useful to expand the entropy expression using the logarithm of products to separate the U and V dependence. One of the things which can be determined directly from this equation is the change in entropy during an isothermal expansion where N and U are constant (implying Q=W). The conditional entropy can be calculated by splitting the dataset into groups for each observed value of a and calculating the sum of the ratio of examples in each group out. The more disordered a system and higher the entropy, the less of a system's energy is available to do work.


Entropy also describes how much energy is not available to do work.
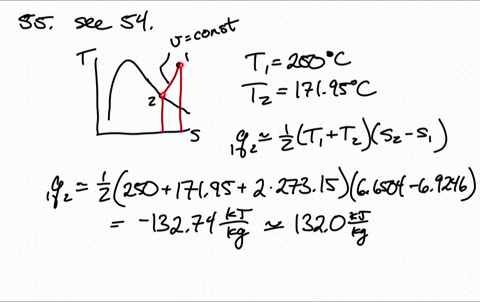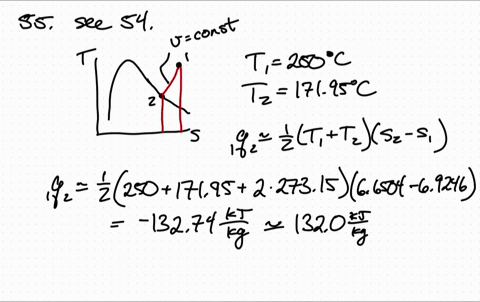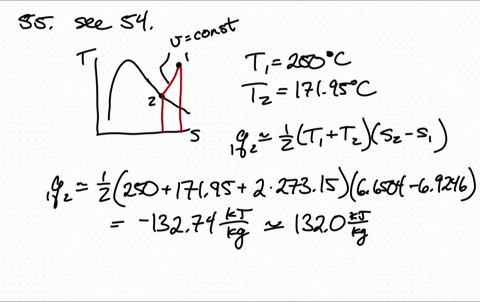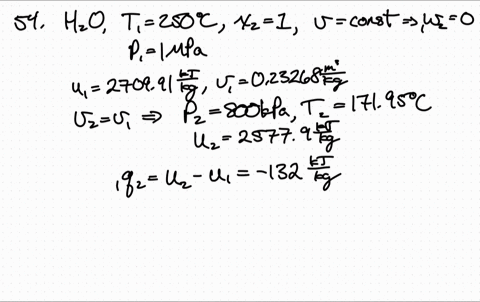
Less Work is Produced by a Given Heat Transfer When Entropy Change is Greater Example 3: Entropy. Entropy is a measure of the disorder of a system. The entropy S of a monoatomic ideal gas can be expressed in a famous equation called the Sackur-Tetrode equation. 15.6 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy of an Ideal Gas Entropy of an Ideal Gas


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
